2 Characteristics Used to Describe Muscle Tissue
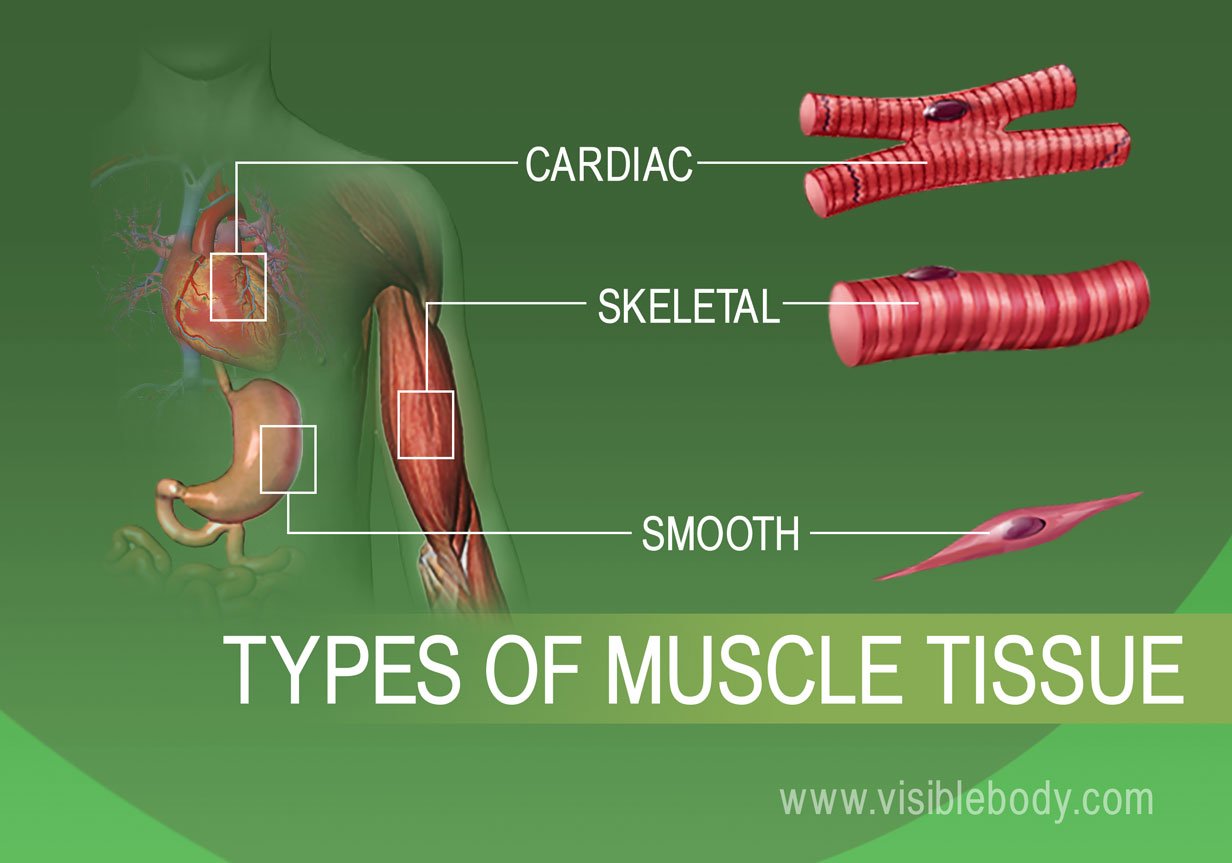
There are three types of muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the heart.

Muscle Tissue And Motion Anatomy And Physiology I
A tissue is a group of cells in close proximity organized to perform one or more specific functions.

. Without much conscious control our muscles. Skeletal muscle cardiac muscle and smooth muscle Figure 72. There are four basic tissue types defined by their morphology and function.
Muscular tissue is a specialized tissue in animals which applies forces to different parts of the body by contraction. Most of the bodys skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton. Tap again to see term.
Skeletal muscle cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. TYPES OF MUSCLE TISSUE. Epithelial tissue creates protective boundaries and is involved in the diffusion of ions and.
All muscle tissue characteristics. Click again to see term. Multinucleated and peripherally located.
Skeletal muscle cells are long cylindrical multi-nucleated and striated. Skeletal muscle cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. There are three types of muscle tissues in the body.
Practicing yoga is a good example of the voluntary use of the muscular system. Elasticity of muscle fibers is extremely important. Surrounds each skeletal fibercell and ties adjacent fibers together.
Epithelial tissue connective tissue muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Tap again to see term. Skeletal muscle along with cardiac muscle is also referred to.
Skeletal muscle cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Each nucleus regulates the metabolic requirements of the sarcoplasm around it. Muscle tissue consists of cells that are highly specialized for the active generation of force for contraction.
A muscle movement not under conscious control eg. They all exhibit a quality called excitability as their plasma membranes can change their electrical states. Muscle is the tissue in animals that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body.
Muscle cells commonly known as myocytes are the cells that make up muscle tissue. The voluntary muscle of vertebrates which is striated and anchored by tendons to bone is used to effect skeletal movement such as locomotion. Cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the heart and pumps blood.
There are three types of muscle tissue. It is made up of thin and elongated cells called muscle fibers. The four types of tissues are exemplified in nervous tissue stratified squamous epithelial tissue cardiac muscle tissue and connective tissue in small intestine.
You control these voluntary muscles. Our bodys skeleton gives enough rigidity to our body that skeletal muscles can yank and pull on it resulting in body movements such as walking chewing running lifting manipulating objects with our hands and picking our noses. Most of the bodys skeletal muscle produces movement by acting on the skeleton.
Cardiac muscle is involuntary striated muscle that is found in the walls and histological foundation of the heart specifically the myocardiumThe cardiac muscle cells also called cardiomyocytes or myocardiocytes predominantly contain only one nucleus although populations with two to four nuclei do exist. Skeletal muscle has four major functional characteristics. Cardiac skeletal and smooth.
It is contractile Totally unique to this tissue The Muscular System. Cardiac muscle tissue is specifically muscle tissue of the heart. The cytoplasm in the muscle fibers is called sarcoplasm.
Muscle is one of the four primary tissue types of the body and the body contains three types of muscle tissue. Tap card to see definition. It contains a network of membrane called the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
The word Muscles refer to all contractile tissue. It is smooth just like skeletal muscle tissue but has special characteristics that help it. Four Types of Tissue.
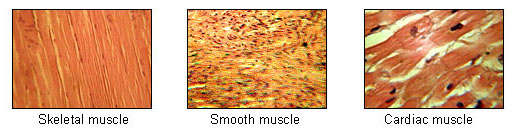
Muscle tissue is a specialized tissue found in animals which functions by contracting thereby applying forces to different parts of the body. Clockwise from nervous tissue LM 872 LM 282 LM 460 LM 800. Page needed The myocardium is the muscle.
1Contractility kon-trak-til i-te is the ability of skeletal muscle to shorten with force. Of connective tissue and enlargement of muscle fibers due to increasing numbers of myofibrils. Micrographs provided by the Regents of University of Michigan Medical School.
Functions of muscle tissue. It is also called striated muscle because transverse bands or striations can be seen in the muscle under the microscope. Bundle of fibers which held together by Endomysium.
Skeletal muscle is also known as voluntary muscle because we can consciously or voluntarily control it in response to input by nerve cells. It is elastic 3. The striped appearance of certain muscle types in which myofibrils are.
The term muscle comes from the Latin word mus which means mouse because the movement of muscles looks like mice running around under our skin. Cylindrical long thick unbranched. Together they support the weight of your body and help you move.
Click again to see term. By contracting the muscle cells pull at their attached ends and cause body parts to move. Muscle is the tissue in animals that allows for active movement of the body or materials within the body.
Click card to see definition. Muscle tissue consists of fibers of muscle cells connected together in sheets and fibers. From top LM 1600 LM 1600 LM 1600.
Some muscle fibers contract quickly and use short bursts of energy fast-twitch muscles. This is achieved by the muscles maintaining a steady electrical field which facilitates the movement of charged ions. Together these sheets and fibers and known as muscles and control the movements of an organisms as well.
All three muscle tissues have some properties in common. These muscles line the heart walls. There are 3 types of muscle cells in the human body.
A Skeletal muscle cells have prominent striation and nuclei on their periphery. The muscular system allows us to move flex and control our bodies. The beating of the heart.
These cells are elongated and can change their shape by becoming shorter and thicker. C Cardiac muscle cells appear striated and have a single nucleus. What are the histological characteristics common to ALL.
Muscle Tissue Definition. Others move slowly such as your back muscles that help with posture. Characteristics of muscle tissue.
Contractility excitability extensibility and elasticity. It controls the movement of an organism. Figure 441 Muscle Tissue.
Lets discuss each in turn. B Smooth muscle cells have a single nucleus and no visible striations. Nucleus of skeletal muscle.
The muscle tissues in our body conduct ion exchange and help carry electrical impulses from the brain and nerves to the body parts and vice-versa. It is excitable 2.

Distinguishing Between The Three Types Of Muscle Tissue Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab Bsb 141
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/cardiac-muscle-3/LNOsY5VQ7ADcaM1g9m5g_Cardiac_Muscle.png)
No comments for "2 Characteristics Used to Describe Muscle Tissue"
Post a Comment